Exhibition of the Czech Reformation in the European context
B Development Context of the Czech Reformation
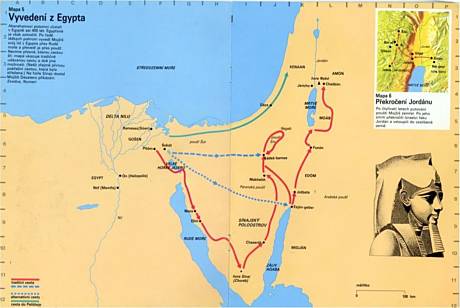
B 1 Trust in One God – the Roots (Israel)
1. Moses is receiving the Ten Commandments Tables from God on Mount Sinai – one artistic expression

2. Mount Sinai (also called Horeb)

4. Archaeological excavations in the locality of Megiddo, the fortified administrative centre of the king Solomon’s empire

5. Qumran – a part of caves where the scrolls of the Old Testament manuscripts (Dead Sea Scrolls) were found

6. A sample of the texts of the scrolls from caves of Qumran

B 2 Trust in One God – the New Branches (Christians)
1. Tabgha – a place where according to the tradition the disciples met resurrected Jesus Christ
– Resurrected Christ feeds his disciples – the image of the Eucharist

2. Archaeological excavations in Capernaum, one centre of Jesus’ activity

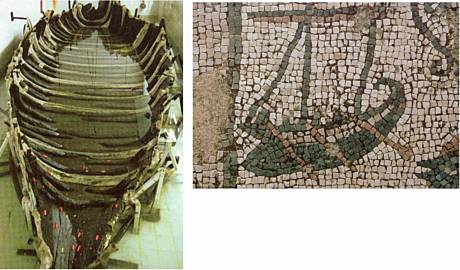
3. A fisherman’s boat from the 1st century AD, found in Lake of Gennesareth
4. The Gethsemane Garden with ancient olives, where Jesus was arrested

5. Archaeological excavations of the former third greatest port of Mediterranean Sea Caesarea Maritima where the way of the non–Judaic Christianity begins
– First Christian Church congregations found in 1st century AD
6. The oldest known fragment of the New Testament and the oldest complete New Testament manuscript – Codex of Sinai

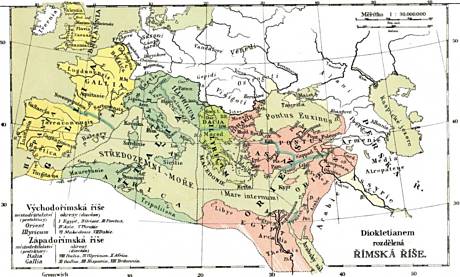
B 3 Christian Organization Assumes the Secular Power – 4th Century
2. Roman catacombs – Christians gathered here as well

3. Emperor Constantine, founder of Constantinople, who issued the Edict of Milan in 313 AD. It was the end of the Christian Church persecution, but also becomes the base of its connection with secular rule.

4. Forum Romanum as a symbol of the disappeared antique Rome

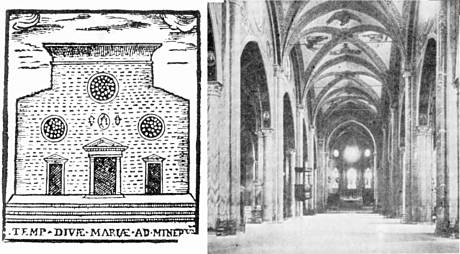
5. Christian temple S. Maria sopra Minerva, built as many others on the foundations of pagan Goddess Minerva temple. In 16th century there were held preludes of horrible mass executions by the Inquisition – auto-da-fé („act of faith“).
6. Pantheon – all pagan gods' temple has preserved because was adapted and used as Christian church.

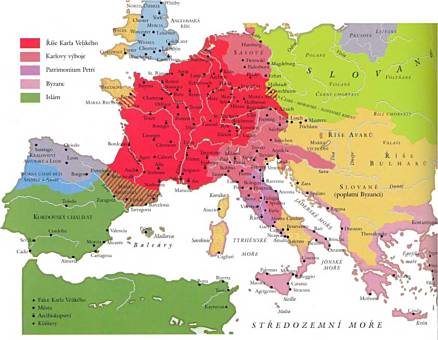
B 4 Church Organization Led by the Pope Controls in the Name of God the Western and Central Europe – 1215
1. Charlemagne was in 800 AD crowned as the Emperor by Roman pope; this date should have been considered as the beginning of the so called Christian Europe.

3. Pope Innocent III, who finished the development of the whole-rule Church institution. He proclaimed that he is smaller than God himself, but greater than all people.

4. During the 4th Council of Lateran in Rome in 1215 the change of the Church into the institution had been completed. Medieval Church proclaimed itself as the mediator between God and human and claimed the authority to control the whole life of an individual as well as the whole society.

5. To keep the obedience and external unity the so called Holy Inquisition was established. It searched for "heretics", tortured them and executed them especially at the stakes. And protected itself by citations from the Bible.

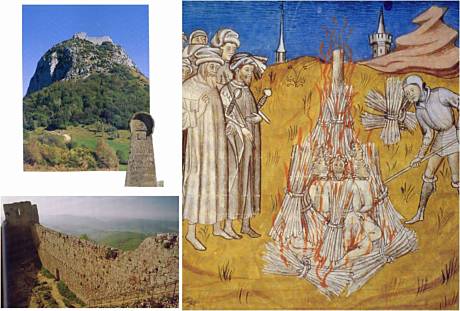
6. The first victims of the whole-rule Church institution were the so called Cathars in Southern France. At the beginning of the 13th century whole areas were slaughtered by a crusade and the region was joined to the north of France.
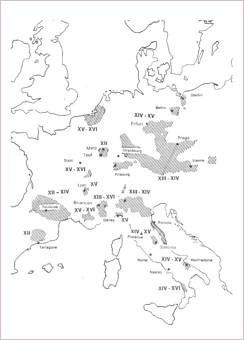
B 5 Heretic’s movements: People Striving for the Return to the Original Character of the Christian Church
1. Ritual text of Cathars (13th century)
– The beginning of John’s Gospel, Waldensian Bible of Carpentras (14th century)

2. Waldensian Eucharist – Naumburg Dome in Thuringia in Germany (13th century)

3. Waldensian candlestick with inscription: "light in darkness"
– Waldensians’ Conference (300th anniversary of the "Return of the Waldensians" in 1689); sign: "Be faithful till death."

5. Jindřichův Hradec (Neuhaus) Castle, its lord led in 1340 the first crusade in the Central Europe against the Waldensians in the South-Eastern Bohemia

6. Landštejn Castle at the borderlands of Bohemia, Moravia and Lower Austria. In its cellars and in the dungeon died the Waldensians.